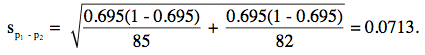Tests of Differences between Proportions (3 of 5)
- (continued) Therefore, z = 0.344/0.0713 = 4.69. A z
table can be used to find that the
two-tailed probability value for a z of 4.69 is less than 0.0001.
If n1 = n2 then p is simply the average of p1 and p2:
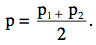
The two p values are averaged since the computations are based on the assumption that the null hypothesis is true. When the null hypothesis is true, both p1 and p2 are estimates of the same value of π. The best estimate of π is then the average of the two p's.
Naturally, if one p is based on more observations than the other, it should be counted more heavily. The formula for p when n1 ≠ n2 is:
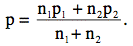
The computations for the example on early childhood intervention are:
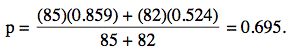
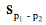 =
=