Tests of Differences between Proportions (2 of 5)
- The second step is to choose a
significance level. Assume the 0.05 level
is chosen.
- The third step is to compute the
difference between the sample proportions. In this example,
p1 - p2 = 73/85 - 43/82 = 0.8588 - 0.5244 =
0.3344.
- The fourth step is to compute p, the
probability (or probability value). It is
the probability of obtaining a difference between the proportions as
large or larger than the difference observed in the experiment.
Applying the general formula to the problem
of differences between proportions
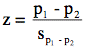
where p1- p2 is the difference between sample proportions and
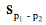
is the estimated standard error of the difference between proportions. The formula for the estimated standard error is:
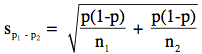
where p is a weighted average of the p1 and p2, n1 is the number of subjects sampled from the first population, and n2 is the number of subjects sampled from the second population.