Factors Affecting Power: Significance level (1 of 2)
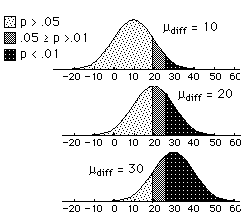
A second important factor affecting power is the significance level chosen. The more conservative (lower) the significance level, the lower the power. Thus, using the 0.01 level will result in lower power than using the 0.05 level. In the example, assuming σ = 50 and N = 25, the null hypothesis is rejected at the 0.05 level if M ≤ -19.6 or M ≥ 19.6 and is rejected at the 0.01 level if M ≤ -25.8 or M > 25.8. (Click here for calculations.)
The figure below shows the power for the 0.05 and 0.01 levels for three values of µdiff. The most darkly shaded area