Tests of μ, Standard Deviation Known (3 of 4)
-
In step five, the probability computed in Step
4 is compared to the significance level stated in Step 2. Since the
probability value (0.028) is less than the significance level (0.05)
the effect is statistically significant.
- Since the effect is significant,
the null hypothesis is rejected. It is concluded that the mean
anxiety score of 10-year-old children with alcoholic parents is
higher than the population mean.
- The results might be described in a
report as follows:
The mean score of children of alcoholic parents (M = 8.1) was significantly higher than the population mean ( µ= 7.0), z = 2.2, p = 0.028.
Summary of Computational Steps
-
Specify the null hypothesis and an alternative hypothesis.
- Compute M = ΣX/N.
- Compute =
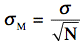 .
.
- Compute
 where M is the
sample mean and µ is the hypothesized value of the
population.
where M is the
sample mean and µ is the hypothesized value of the
population.
- Use a z table to determine p from z.