Tests of Differences between Means, Independent Groups, Standard Deviation Estimated (2 of 8)
- The second step is to choose a
significance level. Assume the .05 level
is chosen.
- The third step is to compute the difference
between sample means (Md). In this example, Mt = 63.89,
MN = 46.79 and Md = MT - MN =
17.10.
- The fourth step is to compute p, the
probability (or probability value) of
obtaining a difference between and the value specified by the null
hypothesis (0) as large or larger than the difference obtained in the
experiment. Applying the general formula,
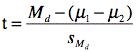
where Md is the difference between sample means, µ1 - µ2 is the difference between population means specified by the null hypothesis (usually zero), and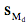 is the
estimated standard error of the difference
between means.
is the
estimated standard error of the difference
between means.