Tests of µ, Standard Deviation Estimated (2 of 4)
-
The first step in hypothesis testing is
to specify the null hypothesis and an alternative
hypothesis. When testing hypotheses about µ, the null hypothesis
is an hypothesized value of µ. In this example, the null hypothesis
is µ = 76. The alternative hypothesis is: µ ≠ 76.
- The second step is to choose a significance level. Assume
the .05 level is chosen.
- The third step is to compute the mean. For
this example, M = 80.85.
- The fourth step is to compute p, the probability
(or probability value) of obtaining a difference
between M and the hypothesized value of µ (76) as large or larger
than the difference obtained in the experiment. Applying the
general formula to this problem,
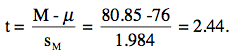
The estimated standard error of the mean (sM) was computed using the formula:
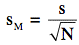
= 8.87/4.47=1.984 where s is the estimated standard deviation and N is the sample size.
The probability value for t can be determined using a t table. The degrees of freedom for t is equal to the degrees of freedom for the estimate of σM which is N - 1 = 20 - 1 = 19. A t table can be used to calculate that the two-tailed probability value of a t of 2.44 with 19 df is 0.025.