Standard Normal Distribution (1 of 2)
The standard normal distribution is a normal distribution with a mean of 0 and a standard deviation of 1. Normal distributions can be transformed to standard normal distributions by the formula:
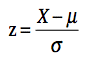
where X is a score from the original normal distribution, μ is the mean of the original normal distribution, and σ is the standard deviation of original normal distribution. The standard normal distribution is sometimes called the z distribution. A z score always reflects the number of standard deviations above or below the mean a particular score is. For instance, if a person scored a 70 on a test with a mean of 50 and a standard deviation of 10, then they scored 2 standard deviations above the mean. Converting the test scores to z scores, an X of 70 would be:
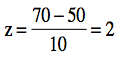
So, a z score of 2 means the original score was 2 standard deviations above the mean. Note that the z distribution will only be a normal distribution if the original distribution (X) is normal.